Pick and Place Machine for PCB Assembly
Pick and place machines are essential tools in modern printed circuit board (PCB) assembly processes. These machines automate the placement of electronic components onto PCBs with exceptional precision and speed. Whether it’s for smartphones, automotive systems, or medical devices, pick and place machines ensure consistent quality in assembling electronic devices.

Introduction to Pick and Place Machines
Importance in Modern PCB Assembly
Pick and place machines have transformed PCB assembly, making it faster, more accurate, and scalable. Before their advent, technicians manually placed components on circuit boards, a time-consuming and error-prone task. Today, automated systems perform this task in a fraction of the time, ensuring the accuracy that modern electronics demand.
How Pick and Place Machines Revolutionized the Industry
By automating the process, these machines have drastically reduced production costs and time. They allow manufacturers to meet the growing demand for smaller, more complex devices by handling microscopic components like surface-mount technology (SMT) chips efficiently
The Basics of PCB Assembly
What is PCB Assembly?
To create functional devices, PCB assembly involves attaching electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits to a blank PCB. It’s a critical step in manufacturing electronic products and requires precision to ensure functionality.
Key Components in PCB Assembly
- Blank PCB: The foundation of the assembly process.
- Electronic Components: Such as ICs, resistors, and capacitors.
- Solder Paste: Used to secure components.
- Pick and Place Machines: Automate component placement.
- Reflow Ovens: Solidify solder paste for secure connections.
Understanding Pick and Place Machines
Definition and Purpose
A pick and place machine is a robotic device used to position electronic components onto a PCB. It uses a combination of vision systems, nozzles, and feeders to pick components and place them accurately on the board.
How It Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Component Feeding: Components are supplied through reels, trays, or tubes.
- Vision Alignment: Cameras align the board and components for precision.
- Picking Components: Robotic arms or heads pick components using vacuum suction or grippers.
- Placing Components: Components are positioned on the board at designated locations.
Types of Pick and Place Machines
Manual Pick and Place Machines
Ideal for small-scale production, these machines require human operators to guide component placement. They are affordable but slower compared to automated options.
Semi-Automatic Machines
These machines combine manual operation with some automation, offering a balance of cost and efficiency. Operators load components, but the machine handles placement.
Fully Automatic Pick and Place Machines
Fully automatic systems are used in high-volume production. They require minimal human intervention and can handle thousands of components per hour with pinpoint accuracy.
Key Features of a Pick and Place Machine
Vision Systems for Precision
Modern pick-and-place machines come equipped with advanced vision systems. These systems use cameras to align the PCB and components with micrometer-level precision. Vision technology ensures that even the tiniest surface-mount devices (SMDs) are accurately placed, reducing defects and ensuring reliability in high-performance electronics.
Component Feeders
Feeders are a crucial part of pick and place machines, as they supply components to the robotic arms. These feeders can handle components in various formats, such as reels, trays, or tubes. Their design ensures a smooth supply of parts, preventing delays and enhancing production efficiency.
Speed and Throughput
One of the most critical factors in evaluating a pick-and-place machine is its speed. Modern machines can place tens of thousands of components per hour, making them indispensable for high-volume manufacturing. Throughput depends on head design, nozzle efficiency, and the machine’s ability to handle simultaneous tasks.
Applications of Pick and Place Machines
Consumer Electronics
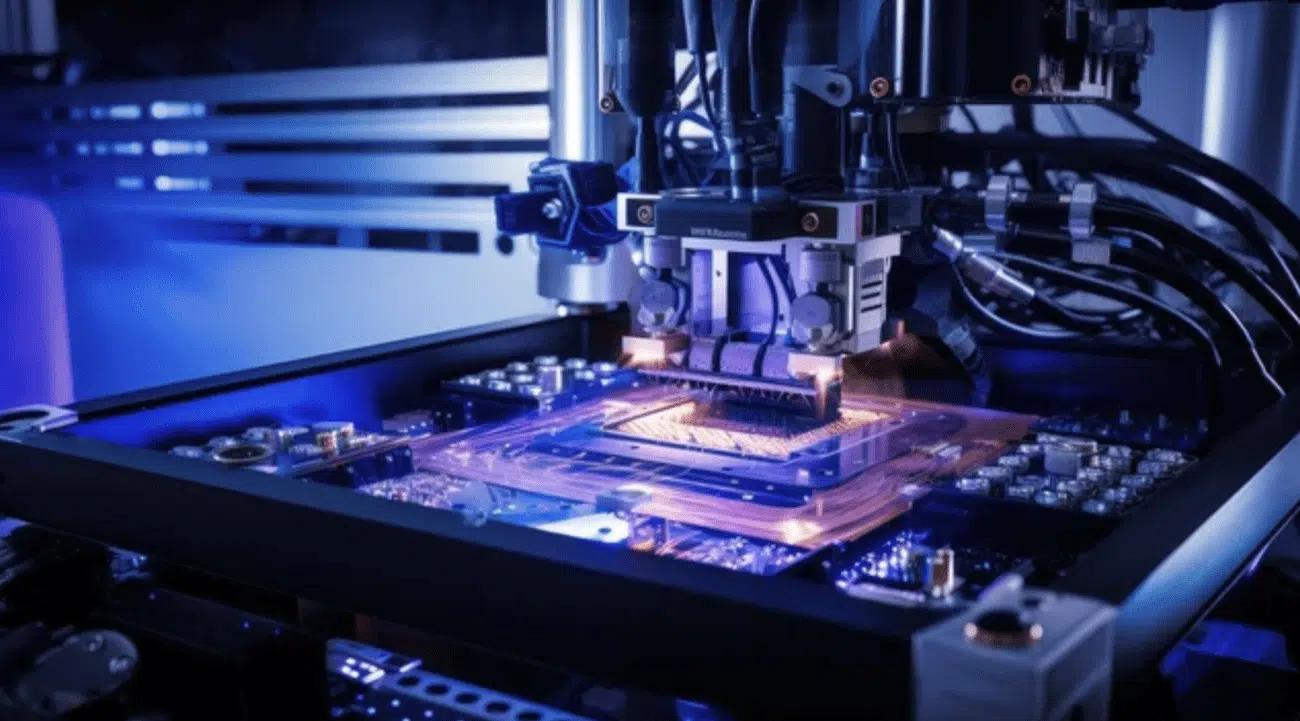
From smartphones to laptops, pick-and-place machines are at the heart of consumer electronics manufacturing. Their ability to handle minute components with speed and accuracy ensures that these devices meet the performance expectations of modern consumers.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector relies heavily on electronic control units (ECUs) and other PCB-based components. Pick and place machines are instrumental in assembling these critical parts, ensuring durability and precision in devices exposed to harsh conditions.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, precision is non-negotiable. Pick and place machines play a vital role in manufacturing devices like pacemakers, diagnostic tools, and monitoring equipment. Their accuracy ensures these devices function flawlessly in life-critical applications.
Advantages of Using Pick and Place Machines
Improved Accuracy and Speed
By automating component placement, pick and place machines significantly reduce the risk of errors that can occur during manual assembly. These machines are incredibly fast, with some models placing thousands of components in just an hour.
Reduced Human Error
Manual assembly is prone to mistakes, especially when dealing with small, delicate components. Pick and place machines eliminate this risk, ensuring every component is placed perfectly, enhancing product quality and consistency.
Scalability for Large Production
As production demands increase, pick and place machines can easily scale to handle higher volumes. They can operate 24/7 with minimal downtime, making them essential for meeting tight deadlines in competitive industries.
Challenges in Using Pick and Place Machines
Initial Investment Costs
One of the primary challenges is the high upfront cost. Advanced pick and place machines, especially fully automated ones, require significant investment. However, this cost is often offset by the long-term benefits of speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
Complexity in Programming
Operating a pick and place machine requires specialized knowledge. Setting up the machine, programming placement patterns, and optimizing performance can be complex and time-consuming, especially for beginners.
Maintenance Requirements
Like any sophisticated equipment, pick and place machines require regular maintenance to function optimally. Components such as nozzles, feeders, and vision systems must be cleaned and calibrated to prevent downtime.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Pick and Place Machine
Production Volume
The scale of production is a significant factor in choosing the right machine. Small businesses may opt for manual or semi-automatic machines, while large-scale manufacturers need fully automated systems capable of handling extensive workloads.
Budget Constraints
While high-end machines offer excellent features, they may be out of reach for some businesses. Striking a balance between cost and functionality is essential to maximize return on investment.
Machine Features
Different machines offer unique features such as multi-head designs, high-speed operations, and compatibility with various component sizes. Selecting a machine with features tailored to specific manufacturing needs is crucial for optimal performance.The Future of Pick and Place Machines
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are shaping the future of pick and place machines. These technologies enable real-time adjustments, predictive maintenance, and enhanced decision-making, making the assembly process smarter and more efficient.
Advanced Robotics in PCB Assembly
The integration of advanced robotics allows pick and place machines to handle even smaller and more complex components. Innovations such as collaborative robots (cobots) enable safer and more flexible operations alongside human workers.
Conclusion
Pick and place machines have become indispensable tools in PCB assembly, ensuring speed, precision, and scalability. By automating the placement of components, they reduce errors, lower production costs, and allow businesses to meet the increasing demand for high-quality electronic devices. As technology evolves, these machines will continue to play a pivotal role in advancing electronics manufacturing.
FAQs
- What is the role of a pick and place machine in PCB manufacturing?
It automates the placement of electronic components onto PCBs, ensuring accuracy, speed, and consistency in assembly. - How does a pick and place machine improve assembly accuracy?
Advanced vision systems and robotic precision enable these machines to place components with micrometer-level accuracy. - Can small businesses afford pick and place machines?
Yes, manual or semi-automatic machines are budget-friendly options for small-scale operations. - What are the maintenance requirements for these machines?
Regular cleaning, calibration of nozzles and feeders, and software updates are essential for optimal performance. - Are there alternatives to pick and place machines in PCB assembly?
Manual assembly is an alternative, but it’s less efficient and prone to errors compared to automated systems.

 Pick and Place
Pick and Place
 Rework Station
Rework Station
 Solder Paste Printers
Solder Paste Printers
 Reflow Ovens
Reflow Ovens
 Reel Storage System
Reel Storage System
 AOI & SPI INSPECTION
AOI & SPI INSPECTION
 Soldering Machines
Soldering Machines
 Insertion Machine
Insertion Machine
 X-ray inspection
X-ray inspection
 PCB Handeling
PCB Handeling
 Depaneling Machine
Depaneling Machine


