The Ultimate Guide to Selective Sodering Machines
Table of Contents
What is a Selective Soldering Machine
A selective soldering device is a piece of specialized equipment that applies solder at specific points on the PCB. Selective soldering is different from wave soldering which involves immersing the entire board in molten metal. This precision reduces waste and the risk of damage while ensuring strong and reliable connections.
These machines are especially useful when assembling PCBs with both surface-mount and through-hole components. These machines are equipped with sophisticated systems for fluxing, preheating and precise soldering, which ensure a smooth assembly process.
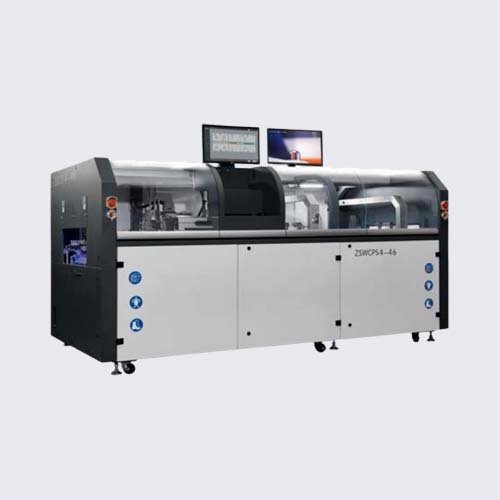

How Do Selective Soldering Machines Work?
Selective soldering is a process that involves a series of steps.
- Flux application: Flux will be applied to the soldering points in order to clean them and to promote solder adhesion. This step ensures robust connections and prevents oxidation.
- Preheating: The PCB will be preheated in order to minimize thermal shock and stabilize temperatures during the soldering procedure.
- Soldering: The machine uses a precisely programmed nozzle to apply molten solder in the designated areas. The soldering is performed with incredible accuracy to ensure that only the targeted areas are soldered.
- Cooling : Solder joints are cooled in order to strengthen and solidify the connections.
This method ensures that solder joints are of high quality and that the components around them are protected from heat damage.
Advantages of Selective Soldering Machines
1. Precision and Accuracy
Selective soldering is incredibly precise. The machines only solder the areas that are required on a PCB. They leave adjacent components unaffected. It is particularly useful for boards that are complex and densely packed.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Selective soldering machines are cost-effective because they reduce material waste and labor. Automation streamlines the entire process and leads to substantial savings.
3. Versatility
They can be used for a variety of PCBs and component types including surface-mount and through-hole devices. These machines are perfect for prototyping and small-scale manufacturing.
4. Environmental Benefits
By using only the required amount of solder, selective soldering reduces waste. Many machines are also designed to use lead-free soldering in order to support environmentally friendly manufacturing.
Applications of Selective Soldering Machines
In industries that require precision and reliability, selective soldering equipment is used.
- Consumer Electronics Devices such as smartphones, laptops and wearables require precision soldering of their PCBs.
- Automotive: Selective soldering is used to ensure robust connections between control modules, sensors and infotainment system.
- Medical Devices: From diagnostic tools and wearable health monitors to diagnostic tools, selective soldering ensures reliability in life-critical applications.
- Aerospace and Defense : To meet the highest quality standards, navigation systems and avionics must be soldered flawlessly.
- Industrial Equipment : Robotics, automated machinery and PCB assemblies rely on selective-soldering to ensure durability.
Types of Selective Soldering Machines
1. Selective Soldering Machines in Line
Inline machines can be integrated into automated production line. These machines are built for high-volume production, and offer consistent quality and speed.
2. Stand-alone Selective Soldering machines
They are ideal for prototyping or small-scale production. These machines are flexible and can handle a variety of board designs.
3. Mini-Wave Soldering Systems
Mini-wave systems target specific areas with a controlled, small wave of molten metal. These systems are perfect for boards that have through-hole components and/or mixed technology.
Key Features to Look For
Consider the following factors when choosing a selective-soldering machine:
- Flux Application System : Assures an even flux distribution, preventing oxidation to enhance solder quality.
- Preheating capabilities: Prevents the thermal stress on PCBs and components when soldering.
- Design of Soldering Nozzle: Choose nozzles with a wide range of sizes and layouts to accommodate PCBs.
- Automation: Machines that have programmable settings, and are monitored in real time offer greater precision and efficiency.
Comparing Selective Soldering with Other Techniques
Selective soldering offers unique advantages over traditional methods:
Wave Soldering
Wave soldering may be faster on simple PCBs, but it lacks the precision required for complex designs. Selective soldering, on the other hand, targets specific points and reduces defects.
Hand Soldering
Hand soldering is flexible for repairs, but it can be time-consuming. It also has a high risk of human error. Selective soldering is a combination of precision and speed.
Reflow soldering
Selective soldering works best for mixed and through-hole designs, while reflow soldering works well for surface-mount components.
Maintaining Your Selective Soldering Machine
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure consistency in performance.
- Clean Nozzles : Maintain a smooth flow of solder by preventing clogging.
- Check Flux Systems: Ensure proper flux application for strong joints.
- Check temperature controls: Maintaining consistent temperatures is essential for quality results.
- Routine Software Upgrades: Update the software regularly to ensure optimal performance.
Future Innovations in Selective Soldering
The technology of selective soldering is rapidly evolving. Automation, Industry 4.0 integration, and improvements in nozzle design set new standards. Smart features such as real-time monitoring of the process and predictive maintenance have become standard. These machines are now even more efficient.
Conclusion
With their precision, versatility, and efficiency, selective soldering machines revolutionize PCB assembly. These machines are unmatched in terms of reliability and quality, whether you work in the consumer electronics, automotive or aerospace industries. Selective soldering is a cornerstone in modern electronics manufacturing.
FAQs
1. How long does a selective soldering machines last?
With proper maintenance, most machines can last up to 10-15 years.
2. Is the selective soldering machine suitable for small scale production?
Yes, standalone machines can be used for small quantities and prototyping.
3. What type of solder is available?
Depending on the application, both lead-free solders and lead-based ones can be used.
4. How are double-sided PCBs handled by these machines?
With precise programming, selective soldering allows for the management of double-sided circuit boards.
5. Is training for the use of selective soldering machines required?
Basic training is required to operate the machine safely and efficiently.
Here are some reliable sources and references for learning more about selective soldering machines:
- IPC Standards
- IPC-A-610: Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies
- IPC J-STD-001: Requirements for Soldered Electrical and Electronic Assemblies
These industry standards provide guidelines for soldering quality and practices.
- Electronics Manufacturing Websites
- SMTnet: A comprehensive source for surface-mount and through-hole soldering techniques.
- PCB Design World: Offers technical articles and news related to soldering and PCB assembly.
- Manufacturer Resources
- Ersa GmbH: A leading manufacturer of selective soldering machines. Their website features product catalogs and technical guides.
- SEHO Systems: Specializes in soldering technologies, with resources on selective soldering (SEHO Systems).

 Pick and Place
Pick and Place
 Rework Station
Rework Station
 Solder Paste Printers
Solder Paste Printers
 Reflow Ovens
Reflow Ovens
 Reel Storage System
Reel Storage System
 AOI & SPI INSPECTION
AOI & SPI INSPECTION
 Soldering Machines
Soldering Machines
 Insertion Machine
Insertion Machine
 X-ray inspection
X-ray inspection
 PCB Handeling
PCB Handeling
 Depaneling Machine
Depaneling Machine


